Blog
Ultimate Guide to NMC Batteries: Everything You Need to Know
2026-01-31 | Calvin
People often compare NMC and LFP batteries, and we’ve also written a detailed comparison. In this article, we delve into the types, safety, performance, usage environment, and market trend of lithium NMC batteries. Let’s start!
Table of Contents
- What Does NMC Stand for in Batteries?
- Different Types of NMC Batteries
- NMC Battery Voltage and Discharge Curve
- NMC Battery Energy Density and Cycle Life
- NMC Battery Safety
- Advantages and Disadvantages of NMC Batteries
- Wide Applications of NMC Batteries
- The Future of NMC Battery Technology and Market Trends
- Conclusion
- FAQs about Lithium NMC Batteries
What Does NMC Stand for in Batteries?
NMC stands for Nickel Manganese Cobalt, which refers to the specific composition of the cathode material used in these batteries. NMC batteries are a type of lithium-ion battery that uses a combination of nickel (Ni), manganese (Mn), and cobalt (Co) in its cathode material. These batteries are known for their high energy density, stability, and relatively long life cycle, making them popular in industries such as electric vehicles (EVs), robotics, and energy storage systems.
Different Types of NMC Batteries
NMC batteries are classified based on the ratios of nickel, manganese, and cobalt. These ratios determine the performance characteristics of each type.
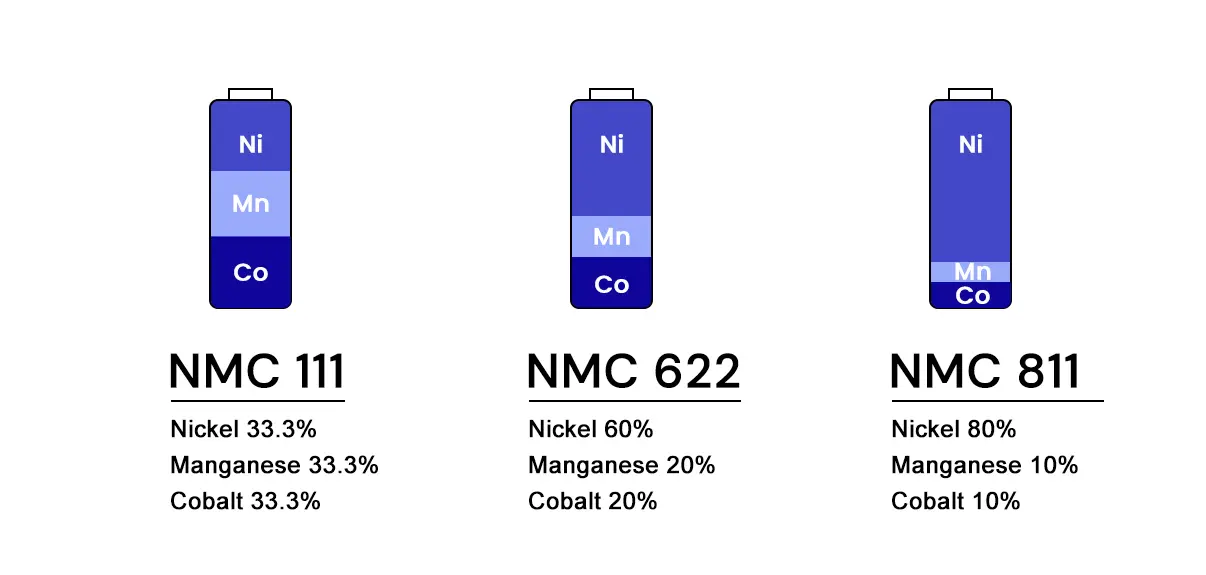
- NMC 111: This type has a ratio of Ni:Mn:Co = 1:1:1. It offers a balance between energy density and safety, with stable performance for around 1,000 to 2,000 charge cycles. However, its energy density is lower compared to other variants (around 160 Wh/kg).
- NMC 532: With a ratio of Ni:Mn:Co = 5:3:2, NMC 532 has an increased energy density of about 180 Wh/kg and better safety than high-nickel types. It is commonly used in cost-sensitive electric vehicles.
- NMC 622: This type has a ratio of Ni:Mn:Co = 6:2:2, providing an energy density above 200 Wh/kg. It strikes a balance between performance and cost and was once a popular choice for EV batteries.
- NMC 811: With a ratio of Ni:Mn:Co = 8:1:1, NMC 811 offers the highest energy density (up to 250 Wh/kg). However, it requires better thermal management to handle higher temperatures, making it ideal for premium EVs like the Tesla Model 3.
NMC Battery Voltage and Discharge Curve
Voltage: NMC batteries have a nominal voltage of 3.7V per cell, with an operating voltage range between 3.0V and 4.2V. This voltage range ensures efficient energy storage and consistent discharge, which is essential for applications requiring stable power outputs.
Discharge Curve: The discharge curve of NMC batteries is characterized by a relatively flat voltage profile. This means that the battery maintains a stable voltage for an extended period before experiencing a sharp drop-off, ensuring a steady power supply for devices and electric vehicles.
NMC Battery Energy Density and Cycle Life
Energy Density: NMC batteries are known for their high energy density. Depending on the specific model (e.g., NMC 532, 622, 811), energy density can range from 150 to 250 Wh/kg, enabling devices such as EVs to achieve long driving ranges with a compact battery size.
Cycle Life: NMC batteries typically last between 1,000 to 2,500 charge cycles, depending on usage conditions. Regular fast charging, excessive charging, and high temperatures can accelerate capacity degradation, so it’s important to maintain optimal charging practices to maximize battery life.
NMC Battery Safety
NMC batteries, like all lithium-ion batteries, are susceptible to safety issues such as thermal runaway, which can result in fires or explosions if the battery is overcharged, damaged, or exposed to extreme temperatures.
Key Safety Features
- Battery Management Systems (BMS): BMS helps monitor battery temperature and voltage, preventing overcharging or deep discharging, which can lead to safety risks.
- Thermal Management: Proper thermal management strategies, such as insulation and cooling systems, ensure the battery remains within safe operating temperatures.
- Structural Optimization: Using fire-retardant coatings and physical isolation within the battery structure helps mitigate risks associated with overheating.
Advantages and Disadvantages of NMC Batteries
Advantages
- High Energy Density: NMC batteries offer superior energy density (150–350 Wh/kg), which is crucial for applications like EVs and drones that require compact, long-lasting power sources.
- Fast Charging: NMC batteries support high current discharge and rapid charging, offering convenience for users who need quick power replenishment.
- Cold Temperature Performance: NMC batteries perform well in low temperatures, making them suitable for use in cold regions.
Disadvantages
- Safety Concerns: High-nickel content in NMC batteries can compromise thermal stability, increasing the risk of thermal runaway and fires in extreme conditions.
- Cost: The raw materials used in NMC batteries, particularly cobalt and nickel, are expensive, which makes the battery costlier compared to other alternatives like LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries.
- High-Temperature Sensitivity: NMC batteries degrade in capacity when exposed to temperatures above 60°C, requiring additional cooling solutions in hot environments.
Wide Applications of NMC Batteries
The versatility of NMC batteries makes them ideal for a wide range of applications:
- Electric Vehicles: NMC batteries power most electric vehicles due to their high energy density, long driving range, and stability.
- Robotics: Humanoid and industrial robots benefit from NMC batteries' compact size and responsive power delivery.
- Power Tools: NMC batteries provide high energy output for tools such as drills and saws, offering long operating times.
- Drones and Aircraft: Their lightweight and high-energy characteristics make NMC batteries perfect for powering drones and other low-altitude aircraft.
- Marine Applications: Used in electric boats and trolling motors, NMC batteries enhance navigation efficiency and battery life for marine industries.
The Future of NMC Battery Technology and Market Trends
The future of NMC battery technology is promising. With ongoing advancements in high-nickel chemistries and new innovations such as solid-state batteries, the energy density and thermal stability of NMC batteries are expected to improve. As industries such as robotics, drones, and electric aviation continue to grow, the demand for high-performance, lightweight, and energy-efficient NMC batteries will rise significantly.
Conclusion
NMC batteries offer exceptional energy density, long cycle life, and fast charging capabilities, making them an essential power source for applications ranging from electric vehicles to robotics. However, safety concerns and high costs remain challenges. To fully harness the potential of NMC batteries, manufacturers must continue to improve thermal management, battery protection systems, and reduce material costs.
FAQs About Lithium NMC Batteries
What is the difference between NMC and LFP batteries?
NMC batteries offer higher energy density and longer driving range, while LFP batteries are safer, more affordable, and have a longer cycle life but with lower energy density.
Are NMC batteries safe?
NMC batteries can be safe when equipped with proper protection systems, such as battery management systems (BMS) and effective thermal management.
How long do NMC batteries last?
On average, NMC batteries last between 1,000 and 2,500 charge cycles, depending on usage conditions.
What industries use NMC batteries?
NMC batteries are commonly used in electric vehicles, drones, robotics, power tools, marine applications, and energy storage systems.
- Next:LiFePO4 Battery Charging FAQ: What You Need to Know
- Previous:How to Reset a Battery Management System (BMS) in Protection Mode
Contact Details
Lithium LiFePO4 Batteries and Lithium LiFePO4 Cells Supplier - LiFePO4 Battery Shop
Contact Person: Miss. Elena Wang
WhatsApp : +8615263269227
Skype : +8615263269227
WeChat :15263269227
Email : info@lifepo4batteryshop.com
All Products
- TC Elcon Charger (0)
- Headway Lithium Battery (6)
- Blade Battery (10)
- Semi Solid State Battery (6)
- A123 Battery (5)
- Sinopoly Battery (7)
- GBS Battery (16)
- CALB Battery (23)
- Cylindrical Cell (8)
- Energy Storage System (0)
- Battery Management System (5)
- Sodium ion Battery Cell (4)
- Lithium Titanate Battery (20)
- Ternary Lithium Battery Cell (11)
- REPT Battery (10)
- BYD Battery (2)
- CATL Battery (15)
- Thunder Sky Winston Battery (21)
- EVE Battery (30)
- LiFePO4 Battery Cell (9)
Certification
Customer Reviews
- I have fond memories of our meeting in Shanghai with LiFePO4 Battery Shop Elena. Your company left a strong impression on me with its impressive growth and professionalism. We both value straightforwardness and honesty, which I believe are the most important qualities in any partnership. I am confident that we can build a successful collaboration based on these shared values. —— Robert from USA
- I've been working with LiFePO4 Battery Shop for years, and their reliability is unmatched. While other suppliers frequently change sales teams, LiFePO4 Battery Shop has consistently provided exceptional service with a stable team. Their commitment to quality and customer support truly sets them apart. —— Henry from Australia



