Blog
The Principle of Lithium-Ion Battery Charging: A Comprehensive Guide
2025-12-16 | Calvin
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are the backbone of modern energy storage, powering everything from smartphones and laptops to electric vehicles. Understanding how these batteries charge and discharge is essential for maximizing their performance and lifespan. In this article, we’ll break down the core principles behind lithium-ion battery charging, the science behind it, and why proper charging methods matter.
How Does Lithium-Ion Battery Charging Work?
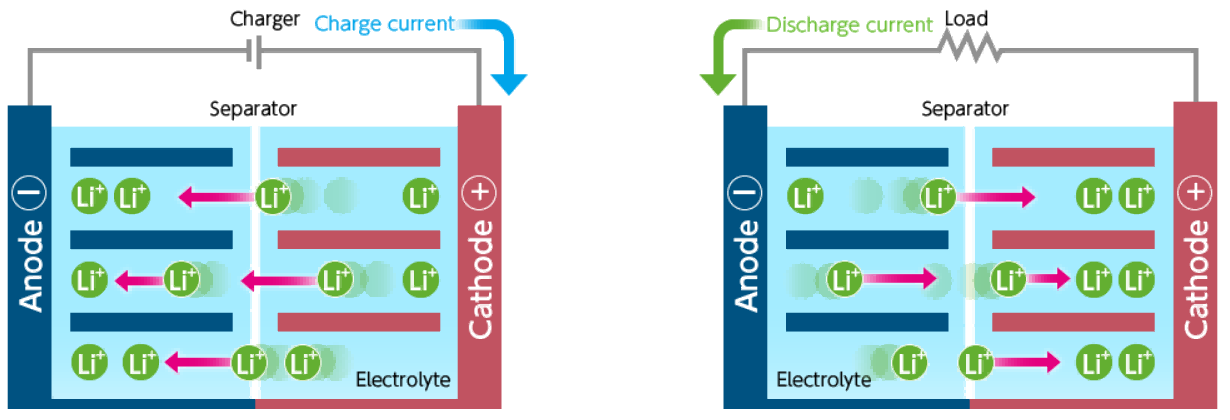
Lithium-ion batteries rely on a simple yet effective principle: lithium ions (Li⁺) move back and forth between the battery's positive and negative electrodes during charging and discharging.
The Charging Process
When charging a lithium-ion battery, lithium ions are released from the positive electrode (often made of lithium metal oxide) and travel through the electrolyte to the negative electrode (typically made of graphite). This process is known as de-intercalation, as the lithium ions leave the positive electrode and become embedded into the micro-structure of the carbon-based negative electrode.
This transition from a low-energy state to a high-energy state stores electrical energy. The more lithium ions that are embedded in the negative electrode, the greater the battery’s capacity to store energy.
The Discharging Process
When the battery is used (i.e., discharging), the lithium ions embedded in the negative electrode (graphite) are released and move back to the positive electrode. This intercalation process powers the device. The more ions that can move back to the positive electrode, the higher the battery's discharge capacity, which is essentially what determines the overall battery life.
The Stages of Lithium-Ion Battery Charging
Charging a lithium-ion battery is more than just connecting it to a power source. Proper charging involves a series of steps to ensure battery safety, efficiency, and longevity. Here are the typical stages of lithium-ion battery charging:
1. Trickle Charge (Low Voltage Pre-Charge)
The trickle charge is the first stage where the battery is charged at a low current to ensure that it is safely initialized. This prevents a sudden rush of current into the battery, which could cause damage, especially when the battery is at a very low charge state.
2. Constant Current Charge
Once the battery voltage reaches a certain threshold, it begins charging at a constant current. This is typically the most energy-efficient stage and ensures the battery charges up quickly without overheating.
3. Constant Voltage Charge
As the battery nears full capacity, the voltage reaches its upper limit. At this point, the charger switches to a constant voltage mode, where the current begins to taper off as the battery reaches its full charge. This step helps prevent overcharging and thermal damage to the battery.
4. Charge Termination
Once the battery reaches its designated full charge level, the charging process stops. If the battery isn’t disconnected, it may begin to overheat or degrade over time, which is why most modern chargers come with built-in safety mechanisms to automatically terminate the charge.
Why Is Lithium-Ion Battery Charging Controlled?
Lithium-ion batteries are sensitive to charging conditions, which is why the charging process must be carefully managed to avoid damage. If charging is not properly controlled, it can lead to a range of problems, such as overheating, reduced battery life, and even dangerous situations like thermal runaway.
One key factor is controlling the current and voltage levels during the charging process. Without a charge management system (typically an IC chip), excessive current can be pushed into the battery, especially when the battery is low on charge. This results in rapid heating, which can shorten the battery’s lifespan and potentially cause permanent damage.
What Is the Ideal Charging Current for Lithium-Ion Batteries?
The charging current of a lithium-ion battery is crucial to its performance and longevity. Typically, lithium-ion batteries can handle a maximum charge rate of 1C. This means that a battery with a capacity of 1,500 mAh (milliamp-hours) can be charged at 1.5A (amps) within one hour. Charging at 1C is ideal for faster charging, but it can generate more heat.
Recommended Charging Rates
For most lithium-ion batteries, the recommended charging current is between 0.2C and 1C. Charging at a higher current (closer to 1C) will reduce charging time but also increase the potential for heat buildup, which can shorten the battery’s overall lifespan.
- For example, charging a 100 Ah battery at a 0.2C rate would require a current of 20A. At 1C, the battery would be charged at a maximum current of 100A.
However, charging rates outside of this range can lead to inefficient charging and could even damage the battery’s internal chemistry.
The Impact of Charging at Lower Rates
On the other hand, charging at a lower current, such as 0.1C, may take longer (up to 10-12 hours) but can help extend the lifespan of the battery. By using a lower charging current, the battery generates less heat, and the electrochemical reactions inside the battery have more time to complete safely.
Differences Between Lithium-Ion and Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) Batteries
Lithium iron phosphate batteries, a variant of lithium-ion batteries, are known for their higher thermal stability and longer lifespan. They can generally handle charging currents up to 1C or even higher (in some cases, up to 15C), making them ideal for power-intensive applications like electric vehicles.
LiFePO4 batteries tend to have a slightly lower energy density than other lithium-ion batteries, but their robustness makes them more suitable for high-discharge-rate applications.
Key Takeaways for Safe and Efficient Lithium-Ion Battery Charging
- Control Charging Current and Voltage: Always ensure the correct charging current and voltage to avoid damage.
- Avoid Overcharging: Lithium-ion batteries should not be overcharged, as this can lead to thermal runaway or a shortened battery lifespan.
- Optimal Charging Rates: For most applications, charging at rates between 0.2C and 1C provides the best balance between speed and battery health.
- Use Proper Chargers: Always use chargers that are designed specifically for lithium-ion batteries, as these come with built-in protections.
Conclusion
Understanding the principles behind lithium-ion battery charging is key to maximizing both performance and lifespan. By following proper charging techniques, including using the correct current and voltage, and ensuring safety protocols, you can extend the life of your devices and reduce the frequency of replacements.
If you're looking to optimize your battery performance, always check your device or battery's user manual for the recommended charging guidelines.
- Next:Exploring the Cycle Life of LiFePO4 Batteries
- Previous:LiFePO4 Battery Temperature Range: What You Need to Know
Contact Details
Lithium LiFePO4 Batteries and Lithium LiFePO4 Cells Supplier - LiFePO4 Battery Shop
Contact Person: Miss. Elena Wang
WhatsApp : +8615263269227
Skype : +8615263269227
WeChat :15263269227
Email : info@lifepo4batteryshop.com
All Products
- Blade Battery (8)
- Semi Solid State Battery (6)
- A123 Battery (5)
- Sinopoly Battery (7)
- GBS Battery (16)
- CALB Battery (22)
- Cylindrical Cell (6)
- Energy Storage System (0)
- Battery Management System (2)
- Sodium ion Battery Cell (3)
- Lithium Titanate Battery (20)
- Ternary Lithium Battery Cell (11)
- REPT Battery (8)
- BYD Battery (2)
- CATL Battery (14)
- Thunder Sky Winston Battery (21)
- EVE Battery (29)
- LiFePO4 Battery Cell (4)
Certification
Customer Reviews
- I have fond memories of our meeting in Shanghai with LiFePO4 Battery Shop Elena. Your company left a strong impression on me with its impressive growth and professionalism. We both value straightforwardness and honesty, which I believe are the most important qualities in any partnership. I am confident that we can build a successful collaboration based on these shared values. —— Robert from USA
- I've been working with LiFePO4 Battery Shop for years, and their reliability is unmatched. While other suppliers frequently change sales teams, LiFePO4 Battery Shop has consistently provided exceptional service with a stable team. Their commitment to quality and customer support truly sets them apart. —— Henry from Australia



