Blog
LiFePO4 Battery Float Voltage Settings and Optimization The Ultimate Technical Guide for 2026
2026-02-07 | Calvin
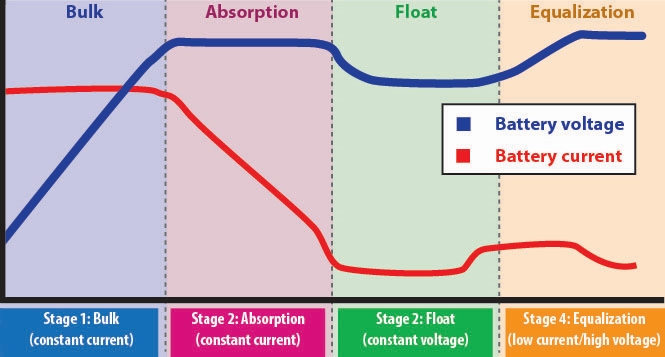
As LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries become the backbone of modern energy systems—from residential solar storage to EVs, RVs, marine power, and telecom backup—proper charging configuration has become a decisive factor in system reliability and battery lifespan.
Among all charging parameters, float voltage is one of the most misunderstood—and most misconfigured—settings.
This guide explains what LiFePO4 battery float voltage is, why it matters, and how to set it correctly, using field-proven practices and industry-aligned recommendations. Whether you are a system integrator, technical buyer, or energy-savvy end user, this article will help you optimize performance while protecting your investment.
What Is a LiFePO4 Battery?
A LiFePO4 battery is a lithium-ion chemistry that uses lithium iron phosphate as the cathode material. Compared with traditional lithium-ion (NMC/NCA) and lead-acid batteries, LiFePO4 is widely adopted due to its:
- Exceptional thermal and chemical stability
- Long cycle life (typically 3,000–6,000 cycles at 80% DoD)
- High safety margin with minimal risk of thermal runaway
- Flat voltage curve and high energy efficiency
These characteristics make LiFePO4 batteries ideal for energy storage systems (ESS), solar applications, EV auxiliary power, off-grid systems, and industrial backup power.
Understanding Float Voltage in LiFePO4 Batteries
What Is Float Voltage?
Float voltage is the constant voltage applied to a fully charged battery to maintain its state of charge (SOC) without continuing aggressive charging.
In simple terms:
- Bulk/absorption charging fills the battery
- Float voltage maintains it
This setting is critical in systems where batteries remain connected to chargers for extended periods, such as solar storage, UPS systems, or telecom infrastructure.
Why Float Voltage Matters for LiFePO4
Although LiFePO4 batteries are more tolerant than lead-acid, they do not benefit from prolonged float charging. Incorrect float voltage can lead to:
- Accelerated calendar aging
- Increased internal resistance
- Gradual capacity fade
- Cell imbalance over time
Correct float voltage helps preserve electrochemical stability, extending service life and maintaining consistent performance.
Recommended LiFePO4 Battery Float Voltage Settings
Float Voltage per Cell
For most LiFePO4 batteries, the recommended float voltage per cell is:
3.20V – 3.30V per cell
This range keeps the battery at a high SOC without stressing the cathode material.
Common System-Level Float Voltages
| Battery Configuration | Nominal Voltage | Recommended Float Voltage |
|---|---|---|
| 4S LiFePO4 | 12.8V | 12.8V – 13.2V |
| 8S LiFePO4 | 25.6V | 25.6V – 26.4V |
| 16S LiFePO4 | 51.2V | 51.2V – 52.8V |
Industry insight: Many LiFePO4 manufacturers now recommend disabling float entirely or setting it at the lowest end of the range for solar and ESS applications where daily cycling occurs.
What Happens If Float Voltage Is Set Incorrectly?
Float Voltage Too High
- Micro-overcharging at the cell level
- Faster electrolyte degradation
- Elevated operating temperature
- Reduced cycle and calendar life
While LiFePO4 chemistry is inherently safe, chronic overvoltage still causes long-term damage.
Float Voltage Too Low
- Battery remains undercharged
- Reduced available capacity
- Poor system reliability during peak demand
- Increased imbalance risk in series packs
Both extremes negatively impact performance and ROI.
How to Set LiFePO4 Float Voltage Correctly
Step-by-Step Best Practices
- Check manufacturer specifications first
Always prioritize OEM datasheets for float voltage recommendations. - Configure via BMS or inverter/charger
Use a charger specifically designed for LiFePO4 chemistry. - Use precision settings
Set voltage values accurately (±0.05V tolerance is ideal). - Consider ambient temperature
Higher temperatures accelerate chemical reactions—slightly reduce float voltage in hot environments. - Verify after rest
After full charge, allow the battery to rest for 2–4 hours before measuring open-circuit voltage. - Monitor periodically
Monthly checks are recommended, especially in new installations.
Key Factors That Influence Float Voltage Optimization
- Temperature: Elevated heat increases degradation risk
- Battery age and SOH: Older batteries may require lower float settings
- Charge profile: Fast charging can temporarily elevate voltage
- Cell balancing quality: Poor balance undermines float effectiveness
Advanced BMS systems with temperature compensation and cell-level monitoring offer significant advantages.
Safety and Compatibility Considerations
- Do not use lead-acid chargers for LiFePO4 batteries
- Ensure charger supports lithium profiles
- Never bypass BMS protection
- Charge in ventilated, temperature-controlled environments
- Inspect periodically for swelling, abnormal heat, or voltage drift
Correct float voltage is as much a safety measure as it is a performance optimization.
LiFePO4 vs Other Battery Technologies: Float Voltage Comparison
| Battery Type | Float Voltage (Per Cell) | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Lead-Acid | 2.25V – 2.30V | High maintenance, sulfation risk |
| NMC / Ternary Li-ion | 4.10V – 4.20V | High energy density, lower safety |
| LiFePO4 | 3.20V – 3.30V | Safe, stable, long cycle life |
LiFePO4 offers the best balance of safety, durability, and operational stability, especially for stationary energy storage.
Practical Maintenance Tips for Longer Battery Life
- Verify float voltage regularly
- Avoid deep discharge below 2.5V per cell
- Operate within 0°C–45°C whenever possible
- Store batteries at ~50% SOC for long-term storage
- Keep firmware and BMS parameters updated
Small adjustments deliver significant lifetime gains.
FAQ
Is float charging necessary for LiFePO4 batteries?
Not always. Many systems perform better with minimal or disabled float.
Can incorrect float voltage damage LiFePO4 batteries?
Yes—especially over long periods.
How often should float voltage be checked?
Monthly during initial operation; quarterly once stable.
Can LiFePO4 batteries be charged in cold weather?
Charging below 0°C should be avoided unless the battery includes low-temperature protection.
Conclusion
Properly setting LiFePO4 battery float voltage is one of the simplest yet most impactful steps you can take to improve system reliability, safety, and long-term value.
With correct configuration, LiFePO4 batteries deliver years of stable, maintenance-free performance, making them the preferred choice for modern energy systems in 2026 and beyond.
- Next:The Ultimate Guide to 36V Batteries: Everything You Need to Know
- Previous:Lithium-Ion Batteries vs. Lithium-Polymer Batteries: Which One is the Best Choice?
Contact Details
Lithium LiFePO4 Batteries and Lithium LiFePO4 Cells Supplier - LiFePO4 Battery Shop
Contact Person: Miss. Elena Wang
WhatsApp : +8615263269227
Skype : +8615263269227
WeChat :15263269227
Email : info@lifepo4batteryshop.com
All Products
- TC Elcon Charger (0)
- Headway Lithium Battery (6)
- Blade Battery (10)
- Semi Solid State Battery (6)
- A123 Battery (5)
- Sinopoly Battery (7)
- GBS Battery (16)
- CALB Battery (23)
- Cylindrical Cell (8)
- Energy Storage System (0)
- Battery Management System (5)
- Sodium ion Battery Cell (4)
- Lithium Titanate Battery (20)
- Ternary Lithium Battery Cell (11)
- REPT Battery (10)
- BYD Battery (2)
- CATL Battery (15)
- Thunder Sky Winston Battery (21)
- EVE Battery (30)
- LiFePO4 Battery Cell (12)
Certification
Customer Reviews
- I have fond memories of our meeting in Shanghai with LiFePO4 Battery Shop Elena. Your company left a strong impression on me with its impressive growth and professionalism. We both value straightforwardness and honesty, which I believe are the most important qualities in any partnership. I am confident that we can build a successful collaboration based on these shared values. —— Robert from USA
- I've been working with LiFePO4 Battery Shop for years, and their reliability is unmatched. While other suppliers frequently change sales teams, LiFePO4 Battery Shop has consistently provided exceptional service with a stable team. Their commitment to quality and customer support truly sets them apart. —— Henry from Australia



