Blog
Difference Between On-Board Charger and Off-Board Charger for Electric Vehicles
2025-12-08 | Calvin
Electric vehicle (EV) chargers are crucial devices designed to convert electrical power into the appropriate form for charging the vehicle’s power battery. They play a key role in ensuring that electric vehicles remain operational by efficiently charging the battery. In this article, we’ll explore the differences between on-board and off-board chargers, two essential types of EV chargers, focusing on their fixed positions, power supply modes, and components.
1. Fixed Position
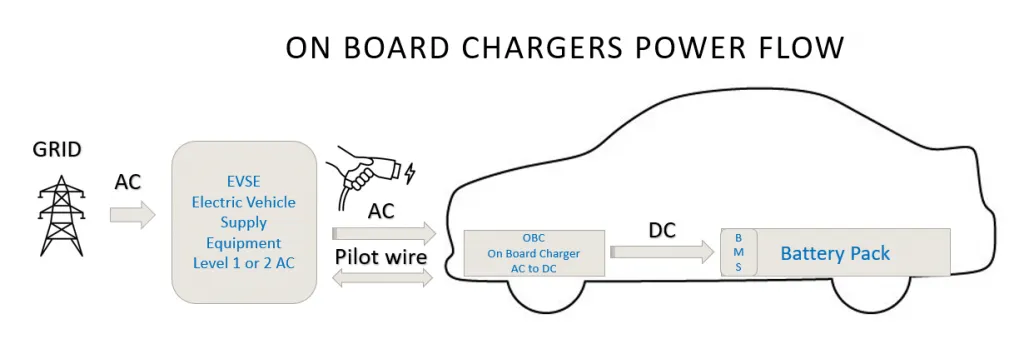
On-Board Charger
An on-board charger is a compact charging device installed directly on the electric vehicle itself. It is constrained by the vehicle's available space and weight limitations, making it smaller, lighter, and lower in power. This compact design allows for convenient, in-vehicle charging but requires compromises in charging speed and power.
Off-Board Charger
In contrast, an off-board charger is located outside the electric vehicle, typically at charging stations. This type of charger is not restricted by space and weight constraints of the vehicle, meaning it can be larger, more powerful, and capable of faster charging. Its larger size allows it to handle high-powered charging for quicker turnaround times.
2. Power Supply Modes
On-Board Charger
The on-board charger typically connects to an AC socket (either single-phase 220V or three-phase 380V AC) via a plug and cable. It converts this AC power into the direct current (DC) required to charge the vehicle’s battery. On-board chargers are often referred to as “slow chargers” because they provide low current and charge the battery at a slower rate.
- Advantages: The primary benefit of an on-board charger is convenience. It can be used at any location with an available AC socket, allowing for widespread charging accessibility. Moreover, slow charging helps extend the life of the battery, reducing wear over time.
- Disadvantages: The relatively low power output limits the speed of charging, leading to longer charging times. Additionally, the charger’s size is constrained by the vehicle, which means it cannot provide the same charging capacity as an off-board charger.
Off-Board Charger
Off-board chargers are connected directly to the AC power grid, converting AC to DC power for high-speed vehicle battery charging. These are typically found in DC charging stations and are known as “fast chargers.”
- Advantages: Off-board chargers offer the advantage of high power and large current capacity, enabling much faster charging times. They can quickly recharge the vehicle battery, which is particularly beneficial for drivers on the go.
- Disadvantages: The larger size and higher power capacity of off-board chargers require significant infrastructure investment. These chargers are fixed in place and are not portable. Moreover, frequent use of fast charging can reduce the overall lifespan of the vehicle battery. It is often recommended to prioritize slow charging and use fast charging only when necessary.
3. Components
On-Board Charger
The on-board charger consists mainly of two key components:
- Power Circuit: This includes the AC voltage regulator, transformer, and power transistors. Its primary function is to convert AC power into the DC power needed by the vehicle’s battery.
- Control Circuit: The control circuit enables communication with the vehicle’s Battery Management System (BMS). It adjusts the output voltage and current based on the battery's charge requirements.
Off-Board Charger
The off-board charger is a more complex system and typically includes several key components:
- Power Unit: Converts AC to DC power.
- Control Unit: Regulates the charging process.
- Metering Unit: Measures the power usage for billing and monitoring purposes.
- Charging Interface: Provides the connection to the vehicle’s charging port.
- Power Supply Interface: Connects to the grid for power input.
- Human-Computer Interface: Allows users to interact with the charger (e.g., via a touchscreen or mobile app).
Conclusion
Both on-board and off-board chargers are integral to the operation of electric vehicles. While on-board chargers are compact and convenient, offering slower but more accessible charging, off-board chargers provide high-powered, fast charging capabilities, albeit with higher infrastructure costs. Understanding these differences is crucial when considering the most appropriate charging solution for your needs, whether it’s for personal use or commercial charging stations.
- Next:How Safe Is a LiFePO4 Battery? A Deep Look at Their Safety Features
- Previous:Understanding C-Rate: The Key to Battery Performance
Contact Details
Lithium LiFePO4 Batteries and Lithium LiFePO4 Cells Supplier - LiFePO4 Battery Shop
Contact Person: Miss. Elena Wang
WhatsApp : +8615263269227
Skype : +8615263269227
WeChat :15263269227
Email : info@lifepo4batteryshop.com
All Products
- Blade Battery (6)
- Semi Solid State Battery (0)
- A123 Battery (5)
- Sinopoly Battery (7)
- GBS Battery (16)
- CALB Battery (22)
- Cylindrical Cell (6)
- Energy Storage System (0)
- Battery Management System (2)
- Sodium ion Battery Cell (3)
- Lithium Titanate Battery (20)
- Ternary Lithium Battery Cell (11)
- REPT Battery (8)
- BYD Battery (2)
- CATL Battery (14)
- Thunder Sky Winston Battery (21)
- EVE Battery (29)
- LiFePO4 Battery Cell (4)
Certification
Customer Reviews
- I have fond memories of our meeting in Shanghai with LiFePO4 Battery Shop Elena. Your company left a strong impression on me with its impressive growth and professionalism. We both value straightforwardness and honesty, which I believe are the most important qualities in any partnership. I am confident that we can build a successful collaboration based on these shared values. —— Robert from USA
- I've been working with LiFePO4 Battery Shop for years, and their reliability is unmatched. While other suppliers frequently change sales teams, LiFePO4 Battery Shop has consistently provided exceptional service with a stable team. Their commitment to quality and customer support truly sets them apart. —— Henry from Australia



