Blog
Which is better NMC or LFP for EV?
2025-10-05 | Calvin
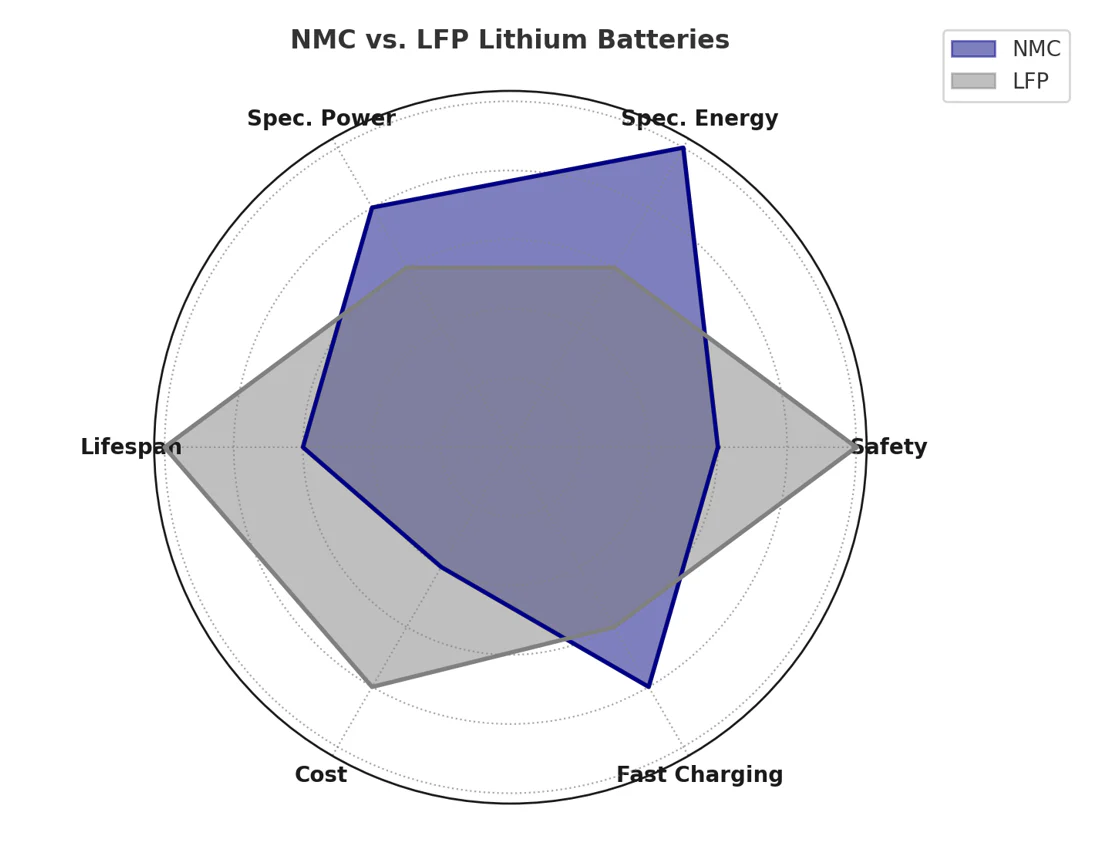
Table of Contents
- What are LFP and NMC Batteries?
- LFP VS NMC Battery: Comparison
- Pros and Cons of LFP and NMC Batteries
- LFP VS NMC Battery for EVs
- LFP VS NMC Battery: Which is Better?
- FAQ about NMC VS LFP Battery
What are LFP and NMC Batteries?
LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) and NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt) batteries are two popular types of lithium-ion batteries with distinct chemical compositions and performance characteristics. LFP batteries use lithium iron phosphate as the cathode material paired with graphite anodes. They offer excellent thermal stability, enhanced safety, and cost efficiency due to the absence of costly metals like cobalt and nickel.
On the other hand, NMC batteries incorporate nickel, manganese, and cobalt in the cathode, which provides higher energy density but at a higher material cost because cobalt and nickel are rare and expensive. Both battery types serve various applications such as drones, robotics, marine equipment, and medical devices, but each excels in different performance aspects.
LFP VS NMC Battery: Comparison
Cost
NMC batteries are generally more expensive due to the use of scarce metals like cobalt and nickel. In contrast, LFP batteries rely on abundant, affordable materials like lithium carbonate, making them a cost-effective option. Additionally, LFP batteries offer a longer cycle life, improving durability and total cost of ownership.
Weight
NMC batteries are lighter, delivering high power output with a compact form factor. This makes them ideal for applications like drones and robotics, where weight is a critical factor.
Energy Density
NMC batteries typically have a higher energy density (180-250 Wh/kg), providing longer runtime and better performance in compact sizes. LFP batteries offer moderate energy density (120-160 Wh/kg), resulting in shorter driving ranges but greater safety.
Safety
LFP batteries are safer due to their chemically stable cathode material, requiring higher temperatures to trigger thermal runaway. NMC batteries heat up faster during failure events, increasing fire risks, and require sophisticated battery management systems for safe operation.
Calendar Degradation
LFP batteries degrade slower over time, losing only 3%-5% capacity annually, whereas NMC batteries lose about 5%-8%. Proper storage conditions, especially avoiding high temperatures, can extend battery lifespan.
Cold Weather Performance
NMC batteries perform better in cold environments, operating efficiently down to -30°C with minimal capacity loss. LFP batteries experience significant performance drops below -20°C, affecting range and charging speed.
Cycle Life
LFP batteries generally last longer, with 2,000-5,000 charge cycles, maintaining over 80% capacity after 3,500 cycles, often translating into over 10 years of use. NMC batteries usually endure 1,000-2,000 cycles, with noticeable degradation after about six years.
Thermal Runaway
LFP batteries demonstrate superior thermal stability, reducing the risk of catastrophic failure. NMC batteries require advanced thermal management systems to prevent overheating and ensure safe operation.
Charging Speed
NMC batteries charge faster due to better tolerance of high current charging, enabling rapid replenishment. LFP batteries are prone to polarization effects at high charge rates, resulting in slower charging speeds.
C-rate Performance
NMC batteries excel in high C-rate scenarios, providing strong instantaneous power output needed for vehicle acceleration and heavy load climbing. LFP batteries deliver steady but less powerful bursts.
Application
NMC batteries suit applications requiring high energy density and compact size, such as premium electric vehicles, drones, and robotics. LFP batteries are preferred where safety, cost efficiency, and long cycle life are prioritized, such as in trolling motors, RVs, and medical devices.
| Performance Aspect | LFP Battery | NMC Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | Medium (120-160 Wh/kg) | High (180-250 Wh/kg) |
| Low-Temperature Performance | Poor | Excellent |
| Cycle Life | 2,000-5,000 cycles | 1,000-2,000 cycles |
| Safety | High | Moderate |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Charging Speed | Slow | Fast |
| Typical Applications | Boats, RVs, Medical Devices | Robots, Drones, Premium EVs |
| Voltage per Cell | 3.2 V | 3.6-3.7 V |
Pros and Cons of LFP and NMC Batteries
Pros of LFP Batteries
- Superior Safety: Highly stable chemistry reduces fire and explosion risks.
- Long Service Life: Can endure 2,000-5,000 cycles, making them ideal for frequent use.
- Cost-Effective: Uses affordable materials, suitable for budget-conscious applications.
Cons of LFP Batteries
- Lower Energy Density: Limits driving range and makes them bulkier for the same power.
- Poor Cold Weather Performance: Significant capacity loss below -20°C.
- Inconsistent Battery Quality: Complex synthesis can lead to variations causing swelling or device issues.
Pros of NMC Batteries
- High Energy Density: Provides longer runtime and better power output.
- Excellent Low-Temperature Performance: Performs well in cold climates down to -30°C.
- High Cell Consistency: Ensures uniform battery pack performance and longevity.
Cons of NMC Batteries
- Shorter Cycle Life: Capacity degrades faster, typically after 1,000-2,000 cycles.
- Higher Cost: Expensive raw materials drive up manufacturing costs.
- Thermal Sensitivity: Requires strict temperature management to prevent overheating.
LFP VS NMC Battery for EVs
In electric vehicles, choosing between LFP and NMC batteries depends on your priorities. LFP batteries are favored for their enhanced safety, longer lifespan, and affordability, making them suitable for city commuting and commercial use. NMC batteries offer superior energy density, better cold-weather performance, and faster charging, ideal for long-distance travel and premium EV models.
If you prioritize durability and safety, especially for long-term ownership (10+ years), LFP batteries are the optimal choice. Conversely, if fast charging, extended driving range, and cold climate performance are essential, NMC batteries are better suited.
LFP VS NMC Battery: Which is Better?
Both LFP and NMC batteries have unique advantages that cater to different needs. LFP batteries excel in safety, longevity, and cost, making them common in commercial vehicles, marine applications, and medical devices. NMC batteries provide higher energy density, faster charging, and superior performance in demanding conditions, dominating in drones, robotics, and premium electric vehicles.
Your choice should align with your usage scenario, budget, and performance requirements.
FAQ about NMC VS LFP Battery
Q1: What is the main difference between LFP and NMC batteries?
LFP batteries use lithium iron phosphate cathodes, offering better safety and longer life but lower energy density. NMC batteries use nickel, manganese, and cobalt cathodes, providing higher energy density but higher cost and shorter lifespan.
Q2: Which battery is safer?
LFP batteries are safer due to stable chemistry and lower risk of thermal runaway.
Q3: Are LFP batteries suitable for electric vehicles?
Yes, especially for city commuting and commercial fleets prioritizing safety and longevity.
Q4: Why are NMC batteries more expensive?
Because of the costly rare metals cobalt and nickel in their cathodes.
Q5: How does temperature affect performance?
NMC batteries perform better in cold weather; LFP batteries lose capacity and charge efficiency in sub-zero temperatures.
Q6: Which battery charges faster?
NMC batteries support faster charging than LFP batteries.
Q7: What is the typical lifespan?
LFP: 2,000-5,000 cycles (~10+ years). NMC: 1,000-2,000 cycles (~6 years).
- Next:What’s the difference between Amp hours (Ah) and Watt hours (Wh)?
- Previous:Tesla Battery Types: A Simple Guide for Model S, 3, X, and Y
Contact Details
Lithium LiFePO4 Batteries and Lithium LiFePO4 Cells Supplier - LiFePO4 Battery Shop
Contact Person: Miss. Elena Wang
WhatsApp : +8615263269227
Skype : +8615263269227
WeChat :15263269227
Email : info@lifepo4batteryshop.com
All Products
- A123 Battery (5)
- Sinopoly Battery (7)
- GBS Battery (16)
- CALB Battery (22)
- Cylindrical Cell (3)
- Energy Storage System (0)
- Battery Management System (2)
- Sodium ion Battery Cell (3)
- Lithium Titanate Battery (16)
- Ternary Lithium Battery Cell (11)
- REPT Battery (8)
- BYD Battery (2)
- CATL Battery (14)
- Thunder Sky Winston Battery (21)
- EVE Battery (29)
- LiFePO4 Battery Cell (4)
Certification
Customer Reviews
- I have fond memories of our meeting in Shanghai with LiFePO4 Battery Shop Elena. Your company left a strong impression on me with its impressive growth and professionalism. We both value straightforwardness and honesty, which I believe are the most important qualities in any partnership. I am confident that we can build a successful collaboration based on these shared values. —— Robert from USA
- I've been working with LiFePO4 Battery Shop for years, and their reliability is unmatched. While other suppliers frequently change sales teams, LiFePO4 Battery Shop has consistently provided exceptional service with a stable team. Their commitment to quality and customer support truly sets them apart. —— Henry from Australia



