Blog
Prismatic vs Pouch vs Cylindrical Lithium-Ion Cells: Which Battery Format Suits Your Application?
2025-07-17 | Calvin
Choosing the right lithium-ion cell format isn’t just a matter of shape—it can fundamentally impact your product’s energy density, thermal behavior, cost, and lifecycle. Whether you're designing an electric vehicle, portable device, or grid storage system, understanding the strengths and trade-offs between prismatic, pouch, and cylindrical cells is essential for optimized performance, cost-efficiency, and reliability.
1. Why Form Factor Matters
Before diving into comparisons, consider the impact of cell format on overall system design:
- Volumetric efficiency (energy per unit volume)
- Gravimetric density (energy per weight)
- Thermal management (cooling efficiency, safety)
- Manufacturing complexity and cost
- Cycle life, mechanical durability, BMS requirements
Let's explore each cell design in detail.
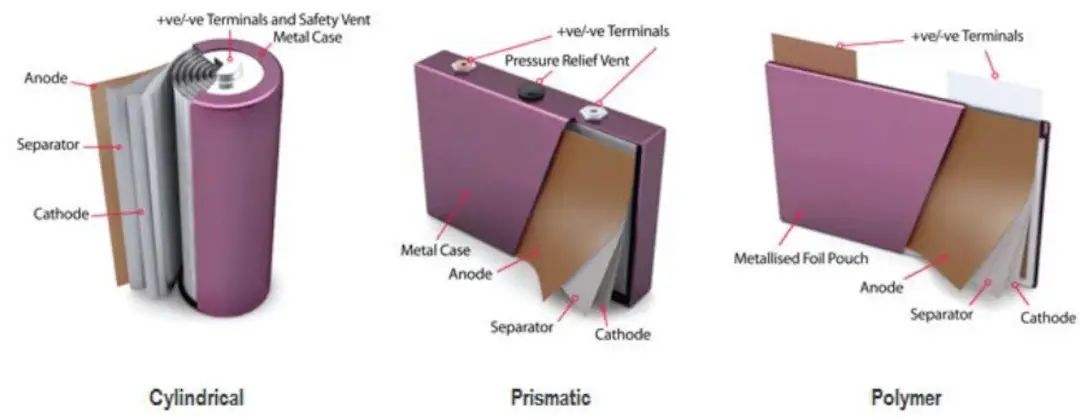
2. Cylindrical Cells: Trusted & Scalable
Structure & Use Cases
- Electrodes spiral-wound inside a metal tube (e.g. 18×65 mm for 18650)
- Powers laptops, power tools, e-bikes, and early Tesla EVs
✅ Advantages
- Proven reliability & mass production: High automation, low scrap, established QC protocols
- Thermal performance: Radial design dissipates heat efficiently, reducing cooling loads by ~14% compared to prismatic
- High C-rate capability: Discharge rates up to 45C (ideal for power‐demanding tools)
- Mechanical durability: Rigid casing withstands vibration and impacts
⚠️ Drawbacks
- Packing efficiency: Cylinders fill ~50–60% of volume versus ~72% for prismatic
- Cell count in packs: More cells increase connections and complexity
- Cycle life: ~800–1,200 cycles at 80% Depth of Discharge (DoD)
3. Prismatic Cells: Compact & Powerful
Structure & Use Cases
- Flat-stacked or flattened-spiral electrodes in rectangular casing
- Ideal for Toyota Prius, Tesla Model Y (4680), home energy storage systems
✅ Advantages
- Superior volumetric efficiency: ~72% volume use, energy densities 160–210 Wh/kg (LFP) up to 255 Wh/kg (NMC)
- Fewer cells per pack: Simplifies wiring, reduces failure points
- Pack integration: Easier to integrate with cooling plates; some designs support active cooling channels
⚠️ Drawbacks
- Thermal management needs: Less natural cooling; requires active or passive systems
- Higher manufacturing cost: Precision stacking, welding, and QC steps add expense
- Cycle life variability: LiFePO4 prismatic cells offer ~2,000+ cycles, but NMC variants differ
4. Pouch Cells: Flexible & Lightweight
Structure & Use Cases
- Flexible aluminum-polymer pouch with sealed electrodes
- Preferred in smartphones, tablets, drones, and lightweight wearables
✅ Advantages
- Lightweight & customizable: No rigid casing, adaptable to compact or odd-shaped designs
- High gravimetric energy density: Often 250–300 Wh/kg
- Lower material cost: Simpler manufacturing, fewer raw materials
⚠️ Drawbacks
- Durability concerns: Vulnerable to swelling, punctures, thermal runaway
- Thermal hotspots: Require advanced cooling strategies; uneven heat distribution can reduce lifespan
- Lower cycle life: Typically ~1,000 cycles versus higher counts in prismatic
5. Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature / Metric | Cylindrical | Prismatic | Pouch |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | 150–280 Wh/kg | 160–255 Wh/kg | 250–300 Wh/kg |
| Volumetric Use | ~50–60% | ~72% | Very high – minimal casing |
| Thermal Behavior | Excellent passive cooling | Good with engineered cooling | Challenging; needs advanced cooling |
| Cycle Life | ~800–1,200 cycles @ 80% DoD | LiFePO4 prismatic >2,000 cycles | ~1,000 cycles |
| Cost per kWh | Lowest upfront due to scale | Moderate—higher cell cost, lower pack cost | Low cell cost, but QC & system costs |
| Mechanical Durability | High (metal casing) | Moderate (rigid casing) | Low—needs external structuring |
| Form Factor Flexibility | Low | Low–medium | High—custom shapes possible |
| Pack Complexity | High (many small cells) | Low (fewer large cells) | Medium—variable size/shape systems |
6. Selecting the Right Cell
| Application | Best Choice | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Power Tools / Industrial | Cylindrical | Balances high discharge rates and durability |
| Automotive EVs | Prismatic / Cylindrical | Prismatic (for space) or cylindrical (software-managed packs like Tesla) |
| Grid / Residential Storage | Prismatic (LFP) | Long cycle life, robust thermal integration |
| Drones, Wearables | Pouch | Light, high energy density, but manage swelling and safety carefully |
| Laptops, Power Banks | Cylindrical / Pouch | Cylindrical for reliability; pouch for ultra-thin design |
Real-World Examples
- Tesla Model S/X used 18650 tubular cells; Model 3/Y transitioned to 21700 and 4680 prismatic/cylindrical mix
- Nissan Leaf pouch design evolution improved NCM energy density from 157 to 174 Wh/kg
- LFP prismatic gaining popularity in Worldwide due to lower cost and safety
7. Conclusion & Action Guide
There’s no universally “best” cell—selection depends on your use-case priorities:
- Prioritize power, durability, and cost? → Choose cylindrical
- Need max volumetric density, fewer cells, pack simplicity? → Choose prismatic
- Require lightweight, thin, shape-flexible battery? → Choose pouch, but plan safety systems
Next Steps
- Define your design constraints: size, weight, lifespan, cost
- Assess your management systems: cooling, monitoring, safety architectures
- Request samples or datasheets from reputable cell manufacturers (e.g. LG, Panasonic, CATL)
- Validate through prototyping and cycle testing under real-world conditions
In the ever-evolving landscape of lithium-ion battery technology, the choice between prismatic, pouch, and cylindrical cells depends on the specific requirements of the application. Each design offers unique advantages, and manufacturers carefully consider factors such as space constraints, flexibility, weight, and cost to determine the most suitable cell type for a given purpose. As technology advances, innovations in lithium-ion cell design continue to drive progress in energy storage solutions across diverse industries.
- Next:Comprehensive Guide to Solid-State Battery Technologies: Polymer vs Oxide vs Sulfide
- Previous:Tesla Battery Types: A Simple Guide for Model S, 3, X, and Y
Contact Details
Lithium LiFePO4 Batteries and Lithium LiFePO4 Cells Supplier - LiFePO4 Battery Shop
Contact Person: Miss. Elena Wang
WhatsApp : +8615263269227
Skype : +8615263269227
WeChat :15263269227
Email : info@lifepo4batteryshop.com
All Products
- A123 Battery (5)
- Sinopoly Battery (7)
- GBS Battery (16)
- CALB Battery (22)
- Cylindrical Cell (3)
- Energy Storage System (0)
- Battery Management System (2)
- Sodium ion Battery Cell (3)
- Lithium Titanate Battery (16)
- Ternary Lithium Battery Cell (11)
- REPT Battery (8)
- BYD Battery (2)
- CATL Battery (14)
- Thunder Sky Winston Battery (21)
- EVE Battery (29)
- LiFePO4 Battery Cell (4)
Certification
Customer Reviews
- I have fond memories of our meeting in Shanghai with LiFePO4 Battery Shop Elena. Your company left a strong impression on me with its impressive growth and professionalism. We both value straightforwardness and honesty, which I believe are the most important qualities in any partnership. I am confident that we can build a successful collaboration based on these shared values. —— Robert from USA
- I've been working with LiFePO4 Battery Shop for years, and their reliability is unmatched. While other suppliers frequently change sales teams, LiFePO4 Battery Shop has consistently provided exceptional service with a stable team. Their commitment to quality and customer support truly sets them apart. —— Henry from Australia



