News
Tesla and LG Begin Catching Up on LFP Battery Technology
2025-05-25 | Calvin
Overseas battery companies are starting to address their shortcomings in lithium iron phosphate (LFP) technology.
Recently, Tesla claimed that its Texas factory has surpassed other external battery suppliers to become the lowest-cost producer in Tesla's battery supply chain. This achievement at Tesla's Texas factory is likely attributable to breakthroughs in its LFP battery technology.
Additionally, at the end of March, LG recruited a core team from former JAC-Volkswagen (JAC-VW) to strengthen its capabilities in the LFP battery sector. In March of this year, the first batch of approximately 20 former JAC-VW employees began joining LG Energy Solution's Nanjing factory, primarily taking on R&D roles.
The latest data from Gaogong Industry Research (GGII) shows that from January to February 2025, the global market share of LFP power batteries exceeded that of ternary batteries for the first time, reaching 49.9%. Data from China's General Administration of Customs also indicates that LFP exports in January 2025 hit a record high of 1,221 tons, a 34% increase from December 2024 and a staggering 916% year-over-year growth.
The importance of LFP battery technology is growing worldwide.
On April 7, Tesla announced during its Q1 2025 internal meeting that its 4680 battery production line had surpassed external suppliers in cost efficiency.
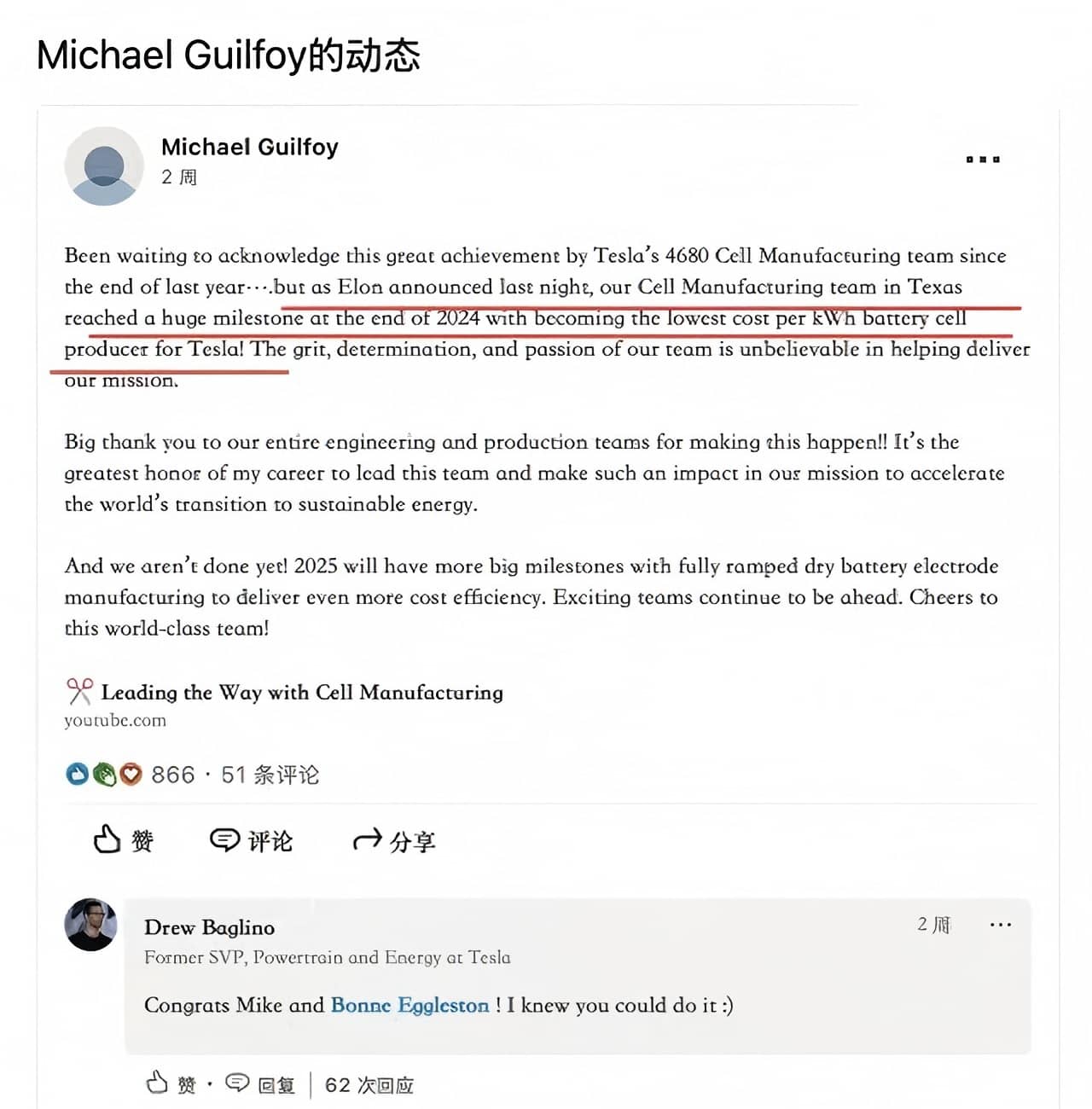
Michael Guilfoy, Tesla's battery manufacturing lead at the Texas Gigafactory, stated on LinkedIn that the Texas battery team has become the lowest-cost-per-kWh producer among Tesla's battery suppliers.
Tesla's battery suppliers include Panasonic, LG, CATL, and BYD. CATL and BYD primarily supply prismatic LFP batteries to Tesla, which currently offer the best cost advantage in China, with prices as low as ¥0.3/Wh. The question remains: How did Tesla manage to surpass the production costs of these two Chinese battery giants?
Tesla's Texas factory is the strategic core for its 4680 battery development. Before 2025, the factory achieved mature production of the second-generation 4680 battery (using wet-process cathodes and dry-process anodes, with energy density exceeding 250 Wh/kg), which has been deployed in vehicles like the Model Y and Cybertruck. In July 2024, Tesla further disclosed that its dual dry-process 4680 batteries would enter mass production in Q4, likely at the Texas factory.
However, judging by material BOM costs, it seems unlikely that a ternary-based 4680 battery could undercut the cost of prismatic LFP batteries. Therefore, Tesla's cost advantage may stem from an LFP version of the 4680 battery.
In October 2024, Tesla revealed plans to launch four dual dry-process 4680 battery variants by 2026, with the durable "NC50" model speculated to use LFP chemistry. That same month, Tesla also posted job openings for LFP battery engineers.
Then, in January 2025, Tesla patented an LFP cathode production method. The patent describes a spray granulation technique that combines integrated mixing and waste recycling, bypassing the need for prefabricated metal sulfates from chemical plants. Raw materials are directly mixed into a uniform slurry, then spray-dried to complete both drying and particle formation in one step. This method eliminates multiple cumbersome steps like separation, washing, and filtration while allowing waste materials to be reused, significantly reducing water consumption and waste disposal costs.
Drew Baglino, Tesla's former VP of Powertrain, tweeted that the patent outlines a lower-investment, lower-cost LFP production method capable of undercutting Chinese prices even without tariff considerations.
Another key factor in Tesla's LFP battery development is its technology licensing partnership with CATL.
In March 2024, CATL Chairman Zeng Yuqun publicly stated that CATL was collaborating with Tesla to develop faster-charging batteries. By late 2024, reports indicated that CATL had formed dedicated teams to meet demand from clients like Ford, GM, and Tesla, establishing two entities—LCTK and CATU—for technology licensing and energy storage projects, respectively.
The licensing focuses on innovations in LFP CTP technology, fast charging, and ultra-fast charging systems. CATL is also supplying battery equipment to Tesla's Nevada Gigafactory.
Compared to Tesla, LG's exploration of LFP batteries is more comprehensive, with progress in talent, technology, materials, and market expansion.
On the talent front, LG Energy Solution brought in a core team from former JAC-VW in late March to bolster its LFP capabilities. The first batch of about 20 former employees joined LG's Nanjing factory in March, mainly in R&D roles. The full team will eventually include around 200 people, covering production, sales, and other functions.
Technologically, LG is developing precursor-free LFP cathode materials that reduce costs and environmental impact while improving low-temperature stability through optimized production processes.
For upstream materials, LG signed a long-term supply agreement with China's Lithium Americas (Changzhou) in February 2024 for 160,000 tons of LFP cathode material from 2024 to 2028. By December 2024, the deal expanded to 260,000 tons, with Lithium Americas planning to utilize its Indonesian subsidiary, Asia Pacific Lithium, to expand annual capacity to 120,000 tons.
In market expansion, LG Energy Solution plans to supply LFP batteries to Renault's EV subsidiary, with orders from late 2025 to 2030 expected to total 39 GWh—enough for approximately 590,000 EVs.
Beyond Tesla and LG, global automakers have shown strong interest in LFP technology. Stellantis, GM, Hyundai, and Volkswagen have all announced plans to adopt LFP batteries in entry-level models.
However, geopolitical tensions are increasingly impacting the new energy sector. As a Chinese-dominated technology, LFP exports face uncertainties.
On January 2, 2025, China's Ministry of Commerce updated its "Catalog of Technologies Prohibited and Restricted from Export," explicitly listing "battery cathode material production technology"—including LFP, LMFP, and related material preparation—as restricted for export.
This adjustment aims to prevent the outflow of advanced LFP battery technology, consolidate China's industrial advantage, and address international competition. The policy is currently open for public feedback, with further refinements expected.
- Next: EVE Energy Showcases Cutting-Edge Storage Solutions at Solartech Indonesia 2025
- Previous: Sunwoda’s Consumer Semi-Solid-State Battery Production Exceeds 8 Million Units
Contact Details
Lithium LiFePO4 Batteries and Lithium LiFePO4 Cells Supplier - LiFePO4 Battery Shop
Contact Person: Miss. Elena Wang
WhatsApp : +8615263269227
Skype : +8615263269227
WeChat : 15263269227
Email : info@lifepo4batteryshop.com
All Products
Certification
Customer Reviews
- I have fond memories of our meeting in Shanghai with LiFePO4 Battery Shop Elena. Your company left a strong impression on me with its impressive growth and professionalism. We both value straightforwardness and honesty, which I believe are the most important qualities in any partnership. I am confident that we can build a successful collaboration based on these shared values. —— Robert from USA
- I've been working with LiFePO4 Battery Shop for years, and their reliability is unmatched. While other suppliers frequently change sales teams, LiFePO4 Battery Shop has consistently provided exceptional service with a stable team. Their commitment to quality and customer support truly sets them apart. —— Henry from Australia



